California’s reservoir levels have long been a focal point for environmentalists, policymakers, and residents alike. As one of the most populous states in the United States, California's water supply is critical for agriculture, urban consumption, and ecological preservation. Understanding the current state of reservoir levels and their fluctuations is essential for addressing the challenges posed by climate change and drought conditions.
California has experienced significant variability in its water supply over the years, with reservoir levels often reflecting the state's complex relationship with water management. This article delves into the intricacies of reservoir levels in California, exploring the factors influencing them and the strategies being implemented to ensure sustainable water resources for the future.
By examining historical data, current trends, and expert insights, this article aims to provide a thorough understanding of the importance of reservoir levels in California. Whether you're a concerned citizen, a policymaker, or an environmental enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of California's water systems.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Reservoir Levels in California
- The Importance of Monitoring Reservoir Levels
- Historical Overview of California's Reservoirs
- Current Status of Reservoir Levels
- Factors Affecting Reservoir Levels
- Climate Change and Its Impact on Reservoir Levels
- Water Management Strategies
- Sustainable Practices for Future Reservoir Management
- Challenges Facing Reservoir Levels
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Reservoir Levels in California
California’s reservoir system is a vital component of its water infrastructure, supporting millions of residents, vast agricultural lands, and diverse ecosystems. Reservoir levels in California are closely monitored due to their critical role in managing water resources during periods of drought and excessive rainfall.
Understanding Reservoirs
Reservoirs are artificial lakes created by damming rivers and streams. They serve multiple purposes, including water storage, flood control, and hydroelectric power generation. In California, reservoirs play a crucial role in balancing water supply and demand.
Key Reservoirs in California
Some of the largest reservoirs in California include Shasta Lake, Lake Oroville, and San Luis Reservoir. These reservoirs contribute significantly to the state's water storage capacity and are essential for maintaining agricultural productivity and urban water supplies.
The Importance of Monitoring Reservoir Levels
Monitoring reservoir levels is essential for effective water resource management. It provides valuable insights into the availability of water resources and helps policymakers make informed decisions regarding water allocation and conservation.
Early Warning Systems
By tracking reservoir levels, authorities can implement early warning systems to alert communities about potential water shortages or flood risks. This proactive approach helps mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events.
Historical Overview of California's Reservoirs
The development of California's reservoir system dates back to the early 20th century, with the construction of large dams aimed at harnessing water resources for agricultural and urban use. Over the decades, the state has expanded its reservoir network to meet growing demands.
Significant Milestones
- Construction of Shasta Dam in the 1940s
- Completion of Oroville Dam in the 1960s
- Establishment of the State Water Project
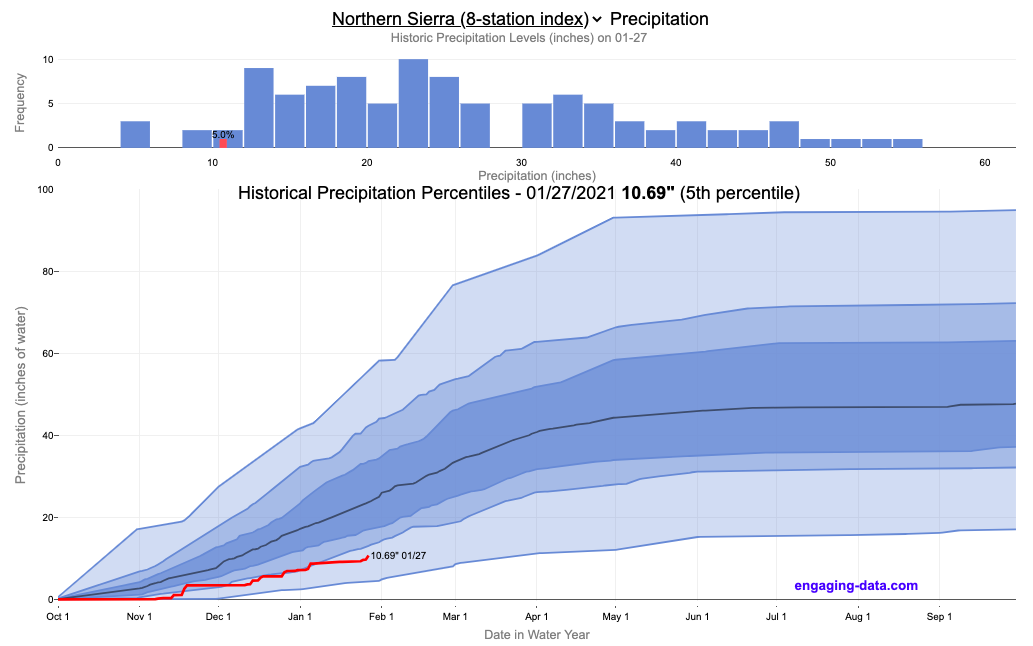
Current Status of Reservoir Levels
As of recent reports, California's reservoir levels fluctuate significantly depending on seasonal variations and weather patterns. While some reservoirs remain at healthy levels, others face challenges due to prolonged drought conditions.
Data and Statistics
According to the California Department of Water Resources, the average statewide reservoir storage is currently at 65% of historical averages. This figure highlights the ongoing need for vigilant water management practices.
Factors Affecting Reservoir Levels
Several factors influence reservoir levels in California, including precipitation patterns, snowpack melt, and water usage. Understanding these factors is key to developing effective water management strategies.
Precipitation Patterns
California's Mediterranean climate results in distinct wet and dry seasons. Variability in precipitation directly impacts reservoir levels, with wet years contributing to higher storage levels and dry years leading to depletion.
Snowpack Melt
The Sierra Nevada snowpack serves as a natural reservoir, releasing water gradually during the spring and summer months. Changes in snowpack volume and melt timing significantly affect downstream reservoir levels.
Climate Change and Its Impact on Reservoir Levels
Climate change poses a significant threat to California's reservoir levels. Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns are expected to reduce snowpack accumulation and increase evaporation rates, further straining water resources.
Adaptation Strategies
To address these challenges, California is exploring adaptive strategies such as enhancing water storage capacity, improving water efficiency, and investing in alternative water sources like desalination and recycled water.
Water Management Strategies
Effective water management is crucial for maintaining reservoir levels in California. Policymakers and water agencies employ a variety of strategies to ensure sustainable water use and conservation.
Water Allocation
Water allocation policies prioritize essential uses, such as drinking water and agriculture, while encouraging conservation efforts across all sectors. This approach helps maximize the efficiency of water distribution.
Sustainable Practices for Future Reservoir Management
Adopting sustainable practices is essential for ensuring the long-term viability of California's reservoirs. Innovations in water technology and community engagement play a vital role in promoting sustainable water management.
Community Involvement
Encouraging public participation in water conservation initiatives fosters a sense of responsibility and collective action. Educational programs and incentive-based programs can inspire individuals and communities to adopt water-saving habits.
Challenges Facing Reservoir Levels
Despite advancements in water management, California's reservoir levels face numerous challenges, including population growth, aging infrastructure, and environmental concerns. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from all stakeholders.
Population Growth
The increasing population in California places additional pressure on water resources, necessitating the expansion of existing infrastructure and the development of new water sources.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Reservoir levels in California are a critical indicator of the state's water health and sustainability. By understanding the factors influencing reservoir levels and implementing effective management strategies, California can ensure a secure water future for its residents and ecosystems.
We invite you to join the conversation by sharing your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Together, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient water system for California. For further reading, explore our related articles on water conservation and environmental stewardship.
References:
- California Department of Water Resources
- U.S. Geological Survey
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration