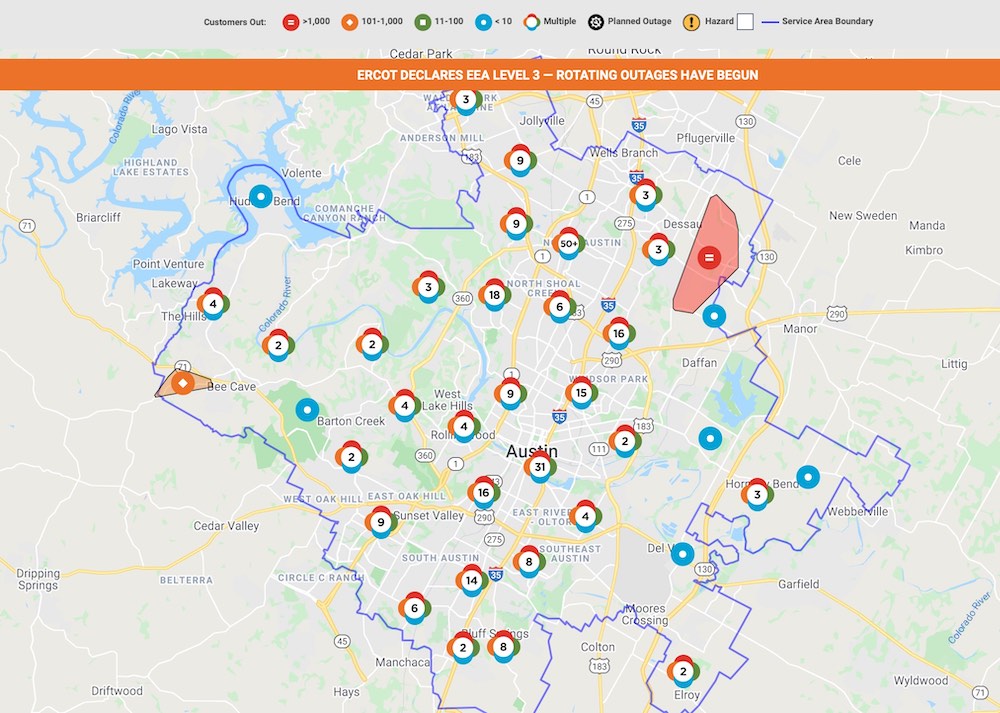
Power outages in Austin have become a growing concern for residents and businesses alike. The city's increasing population and extreme weather conditions have placed significant strain on the local power grid. Understanding the root causes and potential solutions is crucial for ensuring reliable electricity supply in the future.
As one of the fastest-growing cities in the United States, Austin faces unique challenges in maintaining its energy infrastructure. Frequent power outages disrupt daily life, affecting everything from residential comfort to business operations. This article delves into the underlying factors contributing to these outages and explores possible remedies.
Whether you're a homeowner, business owner, or simply someone interested in understanding the energy dynamics of Austin, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights. We'll cover everything from the technical aspects of power distribution to practical tips for dealing with outages.
Table of Contents
- Causes of Power Outage in Austin
- Impact of Power Outages
- Frequency of Power Outages in Austin
- The State of Austin's Power Infrastructure
- Weather-Related Factors
- Solutions to Mitigate Power Outages
- How to Prepare for Power Outages
- Regulations and Policies
- Future Outlook for Austin's Power Grid
- Conclusion
Causes of Power Outage in Austin
Understanding the primary causes of power outages in Austin is essential for developing effective solutions. Several factors contribute to these disruptions, including:
- Weather conditions such as storms, high winds, and ice accumulation.
- Outdated infrastructure that struggles to meet the demands of a growing population.
- Increased energy consumption during peak hours.
Extreme weather events, such as the winter storm in 2021, have highlighted vulnerabilities in the power grid. Aging infrastructure and insufficient investment in modernization further exacerbate the problem.
Weather-Related Causes
Weather plays a significant role in causing power outages. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), severe weather accounts for approximately 70% of all outages nationwide. In Austin, tornadoes, thunderstorms, and ice storms are particularly problematic.
Impact of Power Outages
Power outages have far-reaching consequences for both individuals and businesses. The impact can be categorized into several areas:
- Economic losses due to interrupted business operations.
- Disruption of essential services like healthcare and emergency response.
- Decreased quality of life for residents, especially during prolonged outages.
For example, during the 2021 winter storm, many Austin residents faced dangerous conditions without heat or electricity for days. This highlights the critical need for more resilient infrastructure.
Frequency of Power Outages in Austin
Data from the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) indicates that the frequency of power outages in Austin has been increasing. Between 2018 and 2022, the city experienced an average of 5-7 significant outages per year. This trend underscores the urgency of addressing underlying issues.
A study by the University of Texas found that aging infrastructure and climate change are the primary drivers of this increase. As extreme weather events become more common, the likelihood of outages rises accordingly.
The State of Austin's Power Infrastructure
Austin's power infrastructure faces several challenges. The city's rapid growth has outpaced the development of its energy systems. Key issues include:
- Limited capacity in existing power lines.
- Outdated transformers and substations.
- Inadequate investment in renewable energy sources.
Investing in smart grid technology and renewable energy could significantly improve reliability. The City of Austin has committed to transitioning to 100% renewable energy by 2035, which may help mitigate future outages.
Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the grid is a promising solution. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, renewable energy systems can reduce the frequency and duration of outages. However, challenges remain in terms of storage and distribution.
Weather-Related Factors
Weather remains one of the most significant contributors to power outages in Austin. The city's location in Central Texas makes it vulnerable to a variety of extreme weather events. Key factors include:
- High winds that can damage power lines.
- Ice accumulation during winter storms.
- Heavy rainfall leading to flooding and equipment failure.
Implementing weather-resistant infrastructure and improving emergency preparedness can help reduce the impact of these events.
Winter Storm Preparedness
Preparing for winter storms involves several measures, including:
- Insulating power lines against ice accumulation.
- Developing backup power systems for critical facilities.
- Enhancing communication networks for emergency response.
These steps can help ensure that essential services remain operational during severe weather.
Solutions to Mitigate Power Outages
Addressing the issue of power outages in Austin requires a multi-faceted approach. Potential solutions include:
- Investing in smart grid technology to improve monitoring and response times.
- Expanding renewable energy capacity to reduce reliance on traditional power sources.
- Implementing community-based microgrid systems for localized energy distribution.
Collaboration between government agencies, utility companies, and the private sector is essential for implementing these solutions effectively.
Smart Grid Implementation
Smart grid technology offers numerous benefits, including real-time monitoring, automated response systems, and improved energy efficiency. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), smart grids can reduce outage durations by up to 50%. This makes them a valuable tool in enhancing grid reliability.
How to Prepare for Power Outages
Individuals and businesses can take several steps to prepare for potential power outages:
- Invest in backup power solutions such as generators or battery storage systems.
- Create emergency kits with essential supplies like flashlights, batteries, and non-perishable food.
- Stay informed about local weather conditions and emergency alerts.
Proactive preparation can help minimize the impact of outages on daily life and business operations.
Regulations and Policies
Various regulations and policies govern the operation of Austin's power grid. Key frameworks include:
- ERCOT rules governing electricity distribution.
- State and federal regulations on renewable energy development.
- Local ordinances addressing emergency preparedness.
Compliance with these regulations ensures that utility companies operate safely and efficiently. Advocacy for stronger regulations can further enhance grid reliability.
Future Outlook for Austin's Power Grid
The future of Austin's power grid depends on continued investment in modernization and innovation. Key trends to watch include:
- Growth in renewable energy adoption.
- Development of advanced storage technologies.
- Expansion of smart grid capabilities.
As the city continues to grow, maintaining a reliable and sustainable energy supply will remain a top priority. Public and private sector collaboration will be crucial in achieving this goal.
Conclusion
Power outages in Austin present significant challenges that require immediate attention. By understanding the causes and implementing effective solutions, the city can improve its energy infrastructure and ensure reliable service for all residents. Key takeaways include:
- Weather and aging infrastructure are primary contributors to outages.
- Investing in smart grid technology and renewable energy can enhance reliability.
- Proactive preparation and policy advocacy are essential for minimizing impacts.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into energy and infrastructure topics. Together, we can work towards a more resilient future for Austin's power grid.