Human papillomavirus (HPV) in the mouth is a growing concern worldwide. This condition can lead to significant health issues if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for maintaining oral health and preventing complications.
HPV in the mouth affects thousands of individuals each year. It is essential to recognize the signs early to ensure timely intervention. By exploring the various aspects of this condition, we aim to provide comprehensive insights that promote awareness and prevention.
This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for HPV in the mouth. With a focus on providing actionable information, it serves as a valuable resource for those seeking clarity on this topic.
Table of Contents
- Biography of HPV
- Overview of HPV in the Mouth
- Symptoms of HPV in the Mouth
- Causes of HPV in the Mouth
- How HPV is Transmitted
- Diagnosing HPV in the Mouth
- Treatment Options for HPV in the Mouth
- Preventing HPV in the Mouth
- Statistics and Research
- Frequently Asked Questions
Biography of HPV
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a group of more than 200 related viruses. It is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections globally. HPV can affect various parts of the body, including the mouth and throat. Below is a summary of key details about HPV:
| Scientific Name | Human Papillomavirus |
|---|---|
| Common Types | HPV-16, HPV-18, HPV-6, HPV-11 |
| Transmission | Through skin-to-skin contact, sexual activity |
| Incubation Period | Varies from weeks to years |
| Prevalence | Affects millions worldwide |
Overview of HPV in the Mouth
Understanding the Basics
HPV in the mouth refers to the presence of the virus in oral tissues. This condition can lead to the development of lesions, warts, or even cancer. While not all cases of oral HPV result in severe health issues, early detection is critical for effective management.
Risk Factors
- Engaging in oral sex
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Weakened immune system
- Multiple sexual partners
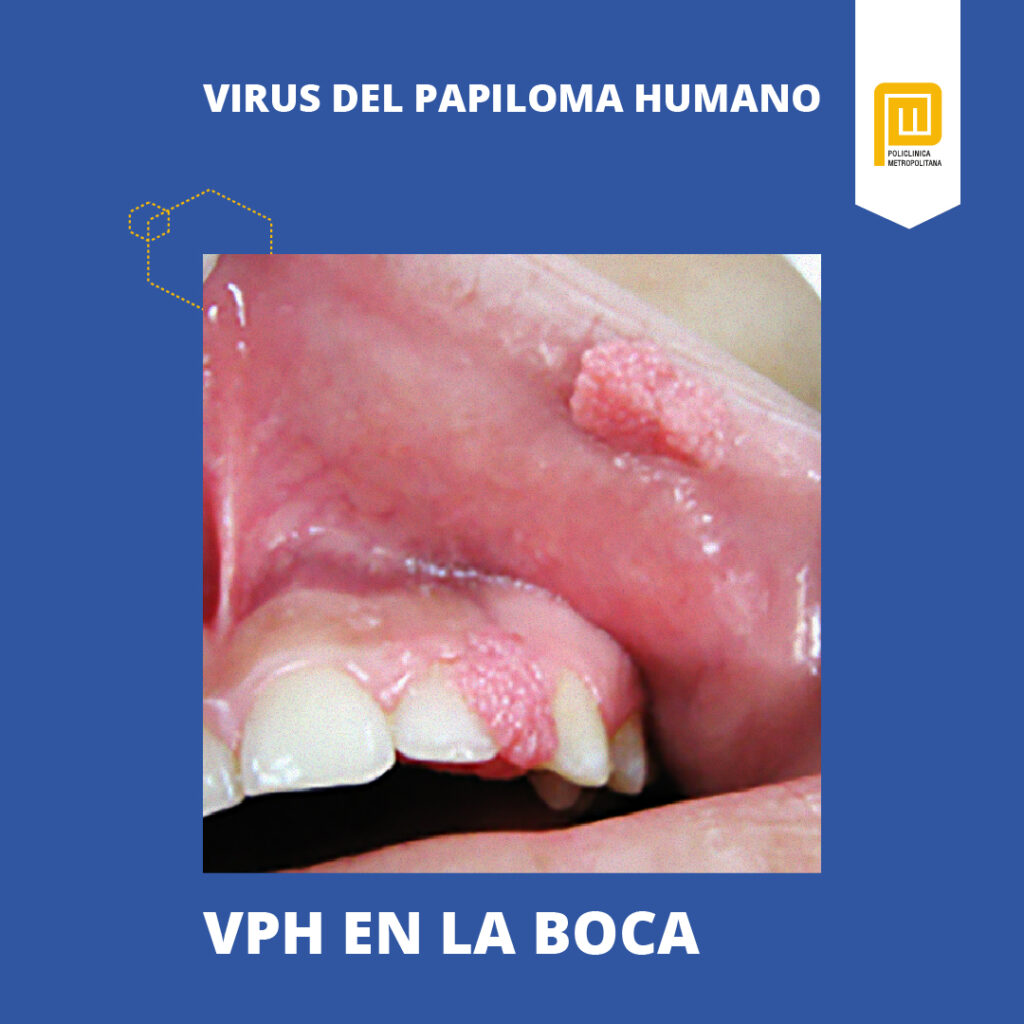
Symptoms of HPV in the Mouth
The symptoms of HPV in the mouth may vary depending on the type of virus and the affected area. Common signs include:
- White or red patches on the tongue, gums, or throat
- Persistent sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Bumps or lesions in the mouth
It is important to note that some individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms, making regular check-ups essential.
Causes of HPV in the Mouth
The primary cause of HPV in the mouth is exposure to the virus through oral sexual activity. Certain high-risk HPV types, such as HPV-16, are more likely to lead to serious health complications. Factors contributing to the transmission include:
- Unprotected sexual contact
- Sharing contaminated objects
- Close physical contact with an infected person
How HPV is Transmitted
Primary Modes of Transmission
HPV spreads primarily through direct skin-to-skin contact. The virus can enter the body through small cuts or abrasions. Oral HPV transmission often occurs during:
- Oral sex
- Kissing (less common)
- Sharing utensils or razors
Preventing Transmission
Using protective barriers during sexual activity and avoiding sharing personal items can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
Diagnosing HPV in the Mouth
Diagnosing HPV in the mouth typically involves a combination of clinical examination and laboratory tests. Dentists and healthcare providers may use the following methods:
- Visual inspection of oral tissues
- Biopsy of suspicious lesions
- HPV DNA testing
Early diagnosis is crucial for preventing the progression of the virus and reducing the risk of complications.
Treatment Options for HPV in the Mouth
Medical Interventions
While there is no cure for HPV, several treatments can manage symptoms and prevent complications. Common approaches include:
- Surgical removal of lesions
- Cryotherapy (freezing)
- Laser therapy
- Antiviral medications
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals opt for complementary treatments, such as herbal remedies or immune-boosting supplements. However, these should only be used under professional guidance.
Preventing HPV in the Mouth
Prevention is key to minimizing the risk of HPV infection. Strategies to protect against oral HPV include:
- Getting vaccinated against HPV
- Practicing safe sex
- Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption
- Regular dental check-ups
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of contracting HPV in the mouth.
Statistics and Research
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 70% of oropharyngeal cancers in the United States are caused by HPV. Studies also indicate that HPV-16 is responsible for the majority of these cases. Ongoing research aims to develop more effective vaccines and treatments to combat the virus.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can HPV in the Mouth Be Cured?
Currently, there is no cure for HPV. However, the immune system can often clear the virus over time. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Is Oral HPV Contagious?
Yes, oral HPV is contagious and can be transmitted through oral sexual activity and other forms of close contact.
Who Should Get the HPV Vaccine?
The HPV vaccine is recommended for individuals aged 9 to 45. It is particularly effective when administered before exposure to the virus.
Conclusion
HPV in the mouth is a significant health concern that requires awareness and proactive management. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments, individuals can take steps to protect themselves and their loved ones. We encourage readers to share this article, consult healthcare professionals, and explore further resources to stay informed.
Feel free to leave a comment or question below. For more information on related topics, explore our other articles on this site.