Gardening in Texas can be both a rewarding and challenging endeavor, especially when you understand the different Texas zones for gardening. Each region in Texas offers unique growing conditions that gardeners need to consider for optimal plant growth. From the arid deserts in the west to the lush forests in the east, Texas's diverse climate zones demand careful planning and knowledge. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or just starting out, understanding these zones is essential for cultivating a thriving garden.
Texas is divided into several gardening zones based on factors such as temperature, rainfall, and soil composition. These zones help gardeners select the right plants that are well-suited to their local environment. By aligning your gardening choices with your specific zone, you can enhance plant health, increase yields, and enjoy a vibrant garden all year round.
In this article, we will delve into the specifics of Texas zones for gardening, offering expert advice and actionable tips to help you create a flourishing garden. Whether you're growing vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to succeed.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Texas Gardening Zones
- USDA Hardiness Zones in Texas
- Climate Diversity in Texas
- Choosing the Right Plants
- Soil Types in Texas
- Watering and Irrigation
- Pest and Disease Management
- Seasonal Gardening Tips
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Texas Gardening Zones
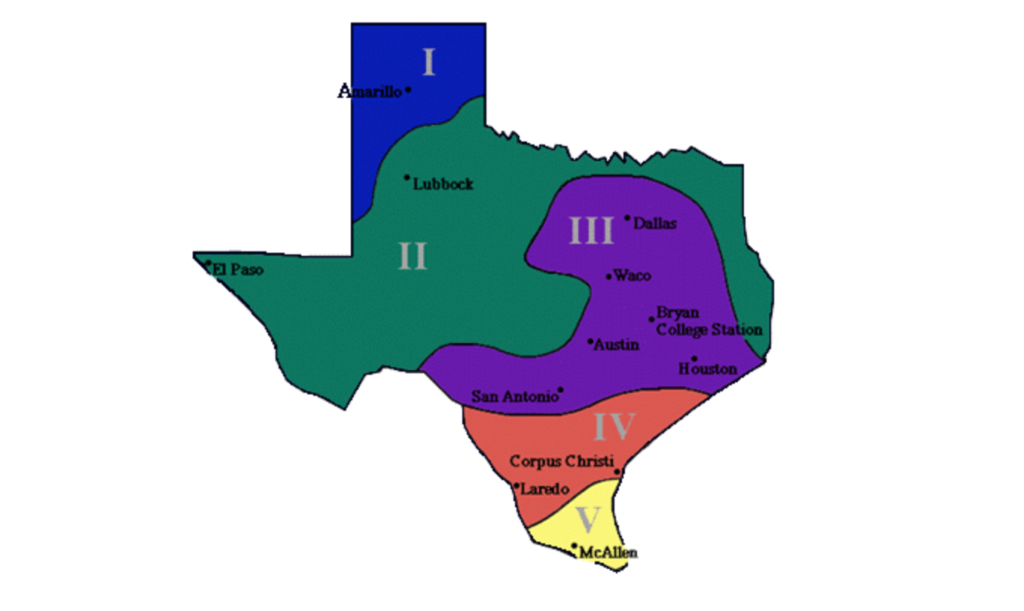
Texas is a vast state with a wide range of climates, making it important for gardeners to understand the specific Texas zones for gardening. The state is divided into different gardening zones based on the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which categorizes areas according to their average annual minimum temperatures. This map serves as a guide for selecting plants that are likely to thrive in your region.
Each zone in Texas presents unique challenges and opportunities for gardeners. For instance, gardeners in the northern part of the state may face colder winters, while those in the southern regions experience milder temperatures year-round. Understanding these differences is crucial for planning and maintaining a successful garden.
Why Gardening Zones Matter
Gardening zones provide gardeners with valuable information about the best times to plant, which plants to choose, and how to care for them. By aligning your gardening practices with your zone, you can maximize plant growth and minimize risks associated with adverse weather conditions.
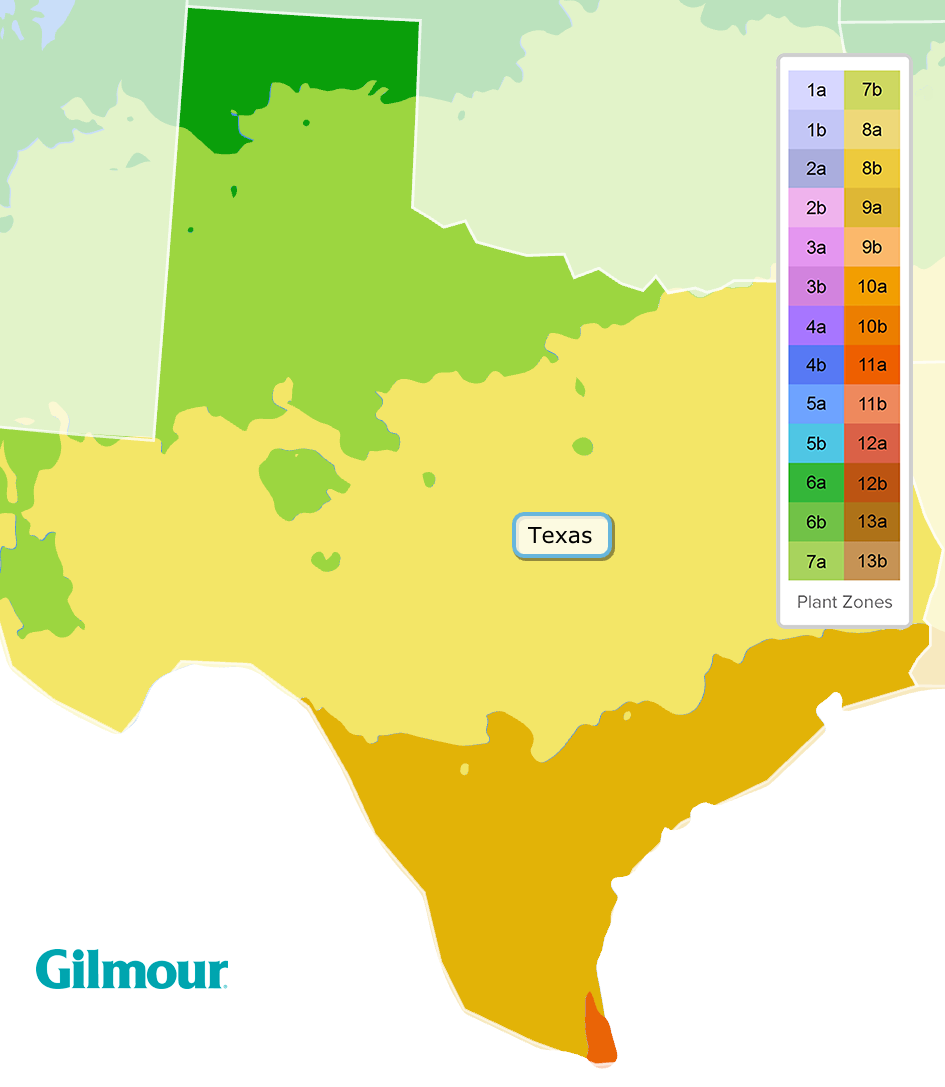
USDA Hardiness Zones in Texas
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides Texas into several zones, ranging from Zone 6b in the northern panhandle to Zone 10a along the Gulf Coast. These zones are determined by the average annual minimum temperatures, which can range from -5°F (-20°C) in Zone 6b to 30°F (-1°C) in Zone 10a.
Zone-Specific Plant Selection
- Zone 6b: Ideal for cold-hardy plants such as evergreen trees and shrubs.
- Zone 7a: Suitable for a variety of vegetables and flowers that can tolerate moderate winters.
- Zone 8b: Perfect for heat-tolerant plants like tomatoes and peppers.
- Zone 9a: Great for subtropical plants such as citrus trees and palms.
- Zone 10a: Ideal for tropical plants that thrive in warm climates.
Climate Diversity in Texas
Texas's climate is as diverse as its geography, with distinct regions that influence gardening practices. From the arid deserts of West Texas to the humid subtropical climate of East Texas, each region requires a different approach to gardening.
Regional Gardening Tips
- West Texas: Focus on drought-resistant plants and efficient irrigation systems.
- Central Texas: Emphasize native plants that can withstand hot summers and occasional freezes.
- East Texas: Prioritize moisture-retentive soils and shade-loving plants.
Choosing the Right Plants
Selecting the right plants is critical for successful gardening in Texas. Native plants are often the best choice, as they are adapted to the local climate and require less maintenance. Additionally, consider the specific needs of each plant, such as sunlight exposure, water requirements, and soil type.
Top Native Plants for Texas Gardens
- Bluebonnets
- Cactus
- Yaupon Holly
- Black-Eyed Susan
Soil Types in Texas
Texas soils vary greatly from sandy loam in the east to clay soils in the central regions. Understanding your soil type is essential for determining the best plants and amendments for your garden.
Improving Soil Health
- Conduct a soil test to identify nutrient deficiencies.
- Add organic matter such as compost to improve soil structure.
- Use mulch to retain moisture and regulate soil temperature.
Watering and Irrigation
Watering is a critical aspect of gardening in Texas, especially in areas prone to drought. Efficient irrigation systems can help conserve water while ensuring plants receive adequate moisture.
Smart Watering Strategies
- Water early in the morning to reduce evaporation.
- Use drip irrigation to deliver water directly to plant roots.
- Monitor rainfall and adjust watering schedules accordingly.
Pest and Disease Management
Pests and diseases can pose significant challenges for Texas gardeners. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies can help minimize damage while promoting a healthy garden ecosystem.
Effective Pest Control
- Encourage beneficial insects such as ladybugs and bees.
- Use organic pesticides sparingly and only when necessary.
- Practice crop rotation to prevent disease buildup.
Seasonal Gardening Tips
Gardening in Texas requires attention to seasonal changes. Each season presents unique opportunities and challenges that gardeners should address to maintain a productive garden year-round.
Spring Gardening
- Plant cool-season crops such as lettuce and spinach.
- Prepare soil for summer plantings.
- Prune trees and shrubs to encourage new growth.
Summer Gardening
- Focus on heat-tolerant plants like okra and melons.
- Monitor water needs closely during hot spells.
- Provide shade for sensitive plants.
Fall Gardening
- Plant fall crops such as carrots and broccoli.
- Divide perennials to promote healthy growth.
- Prepare garden beds for winter.
Winter Gardening
- Protect tender plants from frost.
- Plant winter-hardy vegetables like kale and cabbage.
- Prune fruit trees during their dormant period.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced gardeners can make mistakes when gardening in Texas. Avoiding these common pitfalls can help ensure a successful garden.
- Ignoring your gardening zone when selecting plants.
- Overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other issues.
- Not testing your soil before planting.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Gardening in Texas requires an understanding of the unique zones and climates within the state. By following the tips and strategies outlined in this article, you can create a thriving garden that suits your specific region. Remember to choose the right plants, care for your soil, and manage pests and diseases effectively.
We encourage you to take action by starting your garden today. Share your experiences and tips in the comments below, and don't forget to explore our other articles for more gardening advice. Happy gardening!
Data Sources: USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, Texas A&M AgriLife Extension, National Gardening Association.